With all of the discussion, adoption, and expansion of cloud offerings there is a constant debate that continues to rear its head: Public vs. Private or more bluntly ‘Is there even such thing as a private cloud?’ You typically have two sides of this debate coming from two different camps:
Before we begin let’s start with the basics, The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) definition of cloud:
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared
pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that
can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three service
models, and four deployment models.
Essential Characteristics:
On-demand self-service: A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as
server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human
interaction with each service’s provider.
Broad network access: Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard
mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g.,
mobile phones, laptops, and PDAs).
Resource pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers
using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically
assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand. There is a sense of location
independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact
location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of
abstraction (e.g., country, state, or datacenter). Examples of resources include storage,
processing, memory, network bandwidth, and virtual machines.
Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases
automatically, to quickly scale out, and rapidly released to quickly scale in. To the
consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can
be purchased in any quantity at any time.
Measured Service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging
a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g.,
storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be
monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and
consumer of the utilized service.
Service Models:
Cloud Software as a Service (SaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to use the
provider’s applications running on a cloud infrastructure. The applications are accessible
from various client devices through a thin client interface such as a web browser (e.g.,
web-based email). The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud
infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, storage, or even individual
application capabilities, with the possible exception of limited user-specific application
configuration settings.
Cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to deploy onto
the cloud infrastructure consumer-created or acquired applications created using
programming languages and tools supported by the provider. The consumer does not
manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers,
operating systems, or storage, but has control over the deployed applications and possibly
application hosting environment configurations.
Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The capability provided to the consumer is to provision
processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources where the
consumer is able to deploy and run arbitrary software, which can include operating
systems and applications. The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud
infrastructure but has control over operating systems, storage, deployed applications, and
possibly limited control of select networking components (e.g., host firewalls).
Deployment Models:
Private cloud: The cloud infrastructure is operated solely for an organization. It may be managed
by the organization or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise.
Community cloud: The cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a
specific community that has shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy,
and compliance considerations). It may be managed by the organizations or a third party
and may exist on premise or off premise.
Public cloud: The cloud infrastructure is made available to the general public or a large industry
group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services.
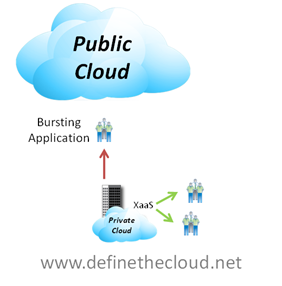
Hybrid cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds (private,
community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized
or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud
bursting for load balancing between clouds).
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/drafts/800-145/Draft-SP-800-145_cloud-definition.pdf
Obviously NIST believes there is a place for private cloud, as do several others, so where does the issue arise?
Public cloud proponents believe in another defining characteristic of cloud computing: Utility Pricing. They believe that the ‘pay for only what you use’ component of public cloud should be required for all clouds, which would negate the concept of private cloud where the infrastructure is paid for up front and has a cost whether or not it’s used. The driver for this is Cloud’s benefit of moving CapEx (capital expenditure) to OpEx (Operating Expenditure.) Because you aren’t buying infrastructure you have no upfront costs and pay as you go for use. This has obvious advantages and this type of utility model makes sense (think power grid in big picture terms, you have metered use.)
Not so fast! There are several key concerns for public cloud that may drive the decision to utilize a private cloud:
These factors must be considered when making a decision to utilize a public cloud. For most organizations they’re typically not roadblocks, but speed bumps that must be navigated carefully.
Private cloud is no unicorn and will be here to stay. For some it will be a stepping stone to a fully public IT model, and for others it will be the solution. Organizations like the federal government have the data security needs to require a private cloud and the size/scale to gain the benefits of that model. Other large organizations may find that private makes more monetary sense. Availability, security, compliance etc. may drive other companies to look at a private cloud model.
Cloud is about cost but it’s more importantly about accelerating the business. When IT can respond immediately to new demands the business can execute more quickly. Both public and private models provide this benefit, each organization will have to decide for itself which model fits their demands.